This example demonstrates the use of the 2D analysis statement where the boundaries are circles.
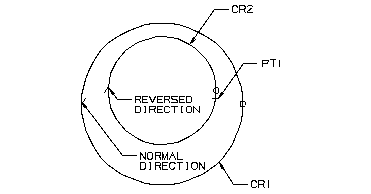
A special condition exists when the main boundary and sub-boundaries are circles because the boundary direction of a circle is normally counterclockwise. You can control this, however, by using a previously defined point in the object list of the boundary statement.
$$
$$ Declarations
$$
ENTITY/CR1,CR2,PT1,BND1,BND2
NUMBER/RETRN(32)
$$
$$ Geometry Definition
$$
CR1 =CIRCLE/2.25,1.75,1.5
CR2 =CIRCLE/2.25,2,1
PT1 =POINT/3.25,1.9
BND1=BOUND/CR1
BND2=BOUND/CR2,PT1
$$
$$ Analysis
$$
ANLSIS/TWOD,BND1,BND2,INCHES,RETRN(1..32)

Using a Point to Reverse the Direction of a Circle Boundary